|
What characterizes life?
Life may be seen as a natural continuation of fusion in
the sun, outsourced to the planet (an "A-Z-illustration"
.here). The force that binds protons gets replaced
by the complementary force binding electrons. It's noteworthy
that it's the unsaturated atoms with shared lack in their
electron shells that build the main structures of life, not
the self-sufficient ones with surplus.
Life as continued fusion is not a merely
banal aspect. The covalent electron bonds as complementary
seems to follow the similar scheme as shown on this site:
- The
genetic code shows astonishing numeral connections
with the 2x2-chain (x = 5-4-3-2-1-0) behind the
periodic
system,
with half this chain times 25 of some unknown reason.
(Scientists with interest in the field of applied mathematics
are invited to search for explanations!)
- The nearly universal genetic code agrees numerically still
closer with a variation of half the same chain: the cubic
roots of 5-4-3-2-1 squared times 100 (the
ES-chain).
- It could be remembered too that flowers have 5-4-3
number plans - surely of some fundamental genetic
reason.
Life from inversions is another aspect proposed here.
It could be mentioned first that 2 times inversion of sum
of all integers 1-110 (110 = the sum of the 2x2-chain)
gives the sum of the amino acids from the genetic code as
periodic number.
- The cell
appears as an inversion of an atom (H, hydrogen) - both regarding
forces and charge but also as it may be in a basic number
of its the genetic code from the inverted mass quotient proton/electron.
- As pointed to in files about biochemistry the inversion
of number 7 seems able to give a code for synthesis
of substance as fatty acids and collagen.
- One suggestion is that life could have its ultimate root
in the 7 so-called "undeveloped" dimensions calculated
with in
the String theory.
About geometries, biologists of profession
often give descriptions in geometrical terms. The same views
here are thus partly about highlighting and formalizing these
aspects.
Biologists' explanations have most often been of the teleological
type: "Why 4 feet?" They are practical for land
living animals. (Yet some fishes got them already in the sea.)
It's naturally assumed here that the evolution contains more
than random mutations and "natural selection", and
the fundamental view sides with theories about a hidden
"black box", here suggested to contain a scheme
of the background model
type or the like if simplified to fundamentals.
The individualization of life remains
perhaps the most difficult to understand Cells appear as a
kind of "singularities", as points of Zero
and Infinity in the same place, 0 and 00
Some numbers:
- 5 - 4 bases (from 2, hypoxanthine - orotic acid): G, A,
U, C + T
- 5 x 4 amino acids (ams) with 4 x 3 x 2 x 1 = 24 different
codons
- 5 histones (proteins on which DNA-chain is rolled upon in
chromosomes)
- Valences for essential elements of life: 5 - 4 - 3 - 2 -
1; P - C - N - O/S - H
- 5 C atoms in the A- and G-bases, 4 in U- and C-bases.
- 5 C in ribose, part of nucleotides.
- 4 - 5 rings in the porphyrins.
- 4 - 5 - 6 cyclic processes have been considered necessary
for "life":
Marquand asked how many chemical processes that a system should
be able to catalyze for it to count as life. Haldane suggested
at least 4, Marquand himself says 5 - 6.
Perhaps the most obvious and essential character in the structure-building
for life is the fact that it is performed by nonmetal atoms,
characterized by mutual lack in relation to the octet rule;
this in opposition to self-sufficient atoms and those with
a surplus of e-. It's mainly constructed of C-N-O,
as if the carbon-nitrogen cycle of nuclear fusion in the sun
just continued, outsourced to planets for transformation into
external relations.
1. Life as the antithesis of entropy:
The way outwards in a dimension chain implies that structure
gradually gets translated into motions, ties as potentials
get broken; it's a trend toward increasing "disorder"
according to views in physical mechanics, equivalent with
direction towards increasing "entropy". (Yet, it
may be discussed if the released motions of macro- and microcosm
in reality are disordered?)
Life implies a shift towards more structure,
synthesis, creation of links, well recognized as the antithesis
of entropy. However, it demands energy from outside to uphold
its life.
Life processes involve both synthesis and
disintegration and can be illustrated by double-direction
within the dimension chain (with development of new levels
proposed as perpendicular to the basic chain).
2. Life a coincidence?
Life is here naturally postulated as a given result from
"laws of Nature", a virtual, built-in possibility
under certain conditions, not a random coincidence. It's assumed
as a given result from the development along the main axes
through the level chain towards increasing complexity. (See
figure at end of this file.)
3."Negative curvature":
It's proposed that the most characteristic feature of Life
could be regarded in terms of "negative curvature inwards"
(cf. "involvement"). This in opposition to the eventual
negative - or rather antipositive - curvature of expanding
vacant space outwards in macrocosm, (This simply expressed
as surfaces growing faster than the cube of the radius.) About
curvature of macrocosm, see file here.)
Most obvious is this feature of antipositive
curvature turned inwards in the development of multicellular
animal organisms (see file Embryology)
but also in eukaryotic unicellular ones. The fast growth of
surfaces occurs inwards and results in multi-shell structures.
Cf. the outward growth of crystals for instance
(If a 5-dimensional unit, developing towards
growing superposed levels, shall get spatial form within 3
dimensions, much has to happen internally out of this contradiction
or tension.)
We could associate to the String
theory and its 7* so called "undeveloped"
dimensions. As a guess they could relate to the ordinary 4
developed ones of ordinary physics in a similar way as mathematical
"conjugates" to each other. Perhaps be the very
root of life!?
*(There are many ways to count dimensions.)
How the single cell first was created is still unknown but
it may be assumed that some kind of a substantiated center
- anticenter polarity between complex molecules had to
be defined within which the positive — negative curvatures
developed, expressed in very general terms.
The turn inwards of the antipositive curvature could eventually
be connected with the pole exchange in last step of our model
in the dimension degree (shortened here d-degree) "0/00"
of Motion.
This redefines d-degree 5 in terms of pure kinetic energy
and may simultaneously imply a kind of feed back mechanism.
4. Life as self mobility:
The "negative curvature" inwards, the expansion
internalized, means more and more enclosed motions according
to the model. One characteristic of life. (Life to regard
as time-loops internally stored into spatial units - or spatial
units transformed and fragmented into "ten thousand"
times?)
However, this would be only one part of
the answer to the "self mobility". The other has
to do with the relation between the single cell and its environment,
center - anticenter, 0- and 00-poles of the whole.
5. Life as ½:
A living organism as the single cell is "haploid"
(½) relative the environment - as a center versus
anticenter in the big level chain leading to birth of a cell.
This essential haploid character concerns all internal levels
and stages of development in the cell. It's expressed as "needs".
"Needs" become potentials originating
from the primary polarization: cell - environment: potentials
that have been differentiated internally in a lot of different
directions, an intricate network of roads. Referring to our
dimension model, the elementary polarity cell - environment
as 0- and 00-poles define Direction, d-degree 4, polarized
inwards/outwards; that's forces for the interaction
of living cells with the surroundings such as inorganic matter,
energy, water, air…
Incorporating of elements from the surroundings
into the cell may be regarded as one aspect on life as developed
through negative curvature inwards. In another context we
have expressed the general principle as a stepwise building-in
of the anticenter pole into the unit defined as center.
One example is the incorporation of metal
ions in cell structures of non-metals, e.g. Mg in chlorophyll.
Compare too our hypotheses that such a principle also may
concern atoms, their structure depending on built-in vacant
space. (If so, the negative curvature inwards should perhaps
not be a feature regarded as restricted to what we generally
call life.)
"Vacant" space can be defined
as antimatter on the atomic level, the environment becomes
antimatter on the biological level.
In general terms the stepwise building-in
of the anticenter is a natural expression for the binding
force between complementary poles.
The chemistry of life is characterized by more or less closed,
"cyclic" processes in communication with the outside
world, and a cyclic process, similar to rotation, means geometrically
more of one-way direction. Increasing one-way direction is
assumed in our model as one main feature in the development
outwards of dimension chains. It implies that directions become
more and more specified.
It's a remarkable fact that not only cells
but also individual molecules can wander between others towards
given addresses - as people in a city on their way towards
certain destinations.
The addresses of pathways can be interpreted
as a complex network of potentials from previous polarization
steps, which means that the molecules are linked on large
distances via underlying levels of space and time - similar
to human memories of past acquaintances and contacts in the
past. Wandering of molecules, governed by needs, becomes in
this way also an expression for the cell being "one half"
on its plentitude of internal levels.
Finally, asymmetries become one result of complementary halvings
of dimension chains in steps towards more of one-way direction.
One example is the selection of L-amino acids among the genetically
coded ones in most organisms. An optical activity that involves
polarization - polarized light.
6. "Instinct" of self-preservation":
That which usually is described as the self-preservation force
of life can simply be the result of and expression for the
binding force between the organism and the environment as
poles out of an original whole: the organism as center one
"half" with navel string downwards the staircase
of levels in Nature with bond to the other half, environment
as anticenter. The lower level is binding force on the superposed
one according to postulates in in the model.
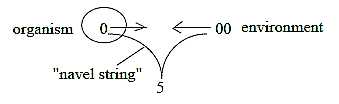 Fig
Li-4-6-2 Fig
Li-4-6-2
7. Reproduction:
As is proposed about light
beams through empty space, the chromosomes (as "lumosomes")
complete themselves from environment, that's from what on
their level is "antimatter", i. e. the manifold
of separate complementary nucleotides, followed by polarizations.
It's on this level an expression for the same pattern as in
an L-wave: → ← → ← → ←...
Generations of cells appear as propagating waves, propagation
of quantified energy packages.
Besides this aspect on reproduction as succession, it's simultaneously
a manifolding of one cell to many, a repetition of the process
with divisions 1-2-4-8... in all directions. If it would be
possible keeping to the analogy of propagating waves, it would
be necessary imagining not only L-waves, in a certain sense
linear, or T-waves as in the same sense 2-dimensional but
waves of a higher dimension. (Compare perhaps where a photon
exists on its way to a screen in quantum mechanics? In some
descriptions "everywhere".)
As far as scientists know, so far, all life springs from other
life - nowadays at least. Does then all life on earth derive
from a single first cell 3-4 billion years ago? It is a rather
curious thought that only a single point on the entire surface
of the Earth would give birth to a cell, assuming that the
cell is a consequence of laws of Nature. Similar chemical
conditions must have existed in many places. Amounts of cells
can have come into existence that were similar because the
same natural laws were applied and the same surrounding conditions.
If so, it would be changes in the environment that later made
life depending on heredity. (Theoretically however, the initial
conditions for emergence of an entire cell should be possible
to produce in laboratories. )
8. Life as demarcated units
Demarcation, individualization, is a vital condition for
life and perhaps the most difficult problem in explaining
the occurrence of cells.
There is in fact the same problem with the
creation of atoms from Big Bang (protons as packets of the
assumed 3 quarks, the 3 divided 2 plus-charged, one minus-charged,
5 → 4 → 3, the 3 divided
2 + 1). Hardly easier to "explain".
Atoms and cells are building stones on very different levels.
Underlying levels represent higher d-degrees than the superposed
ones and are binding forces in relation to these (general
view in the model).
It's logical that the H-atom becomes the
original first integrating force of the cell as polarized
into H+ and e- (as d-degree 5 polarized
into 0- and 00-poles in the model, secondary binding and polarizing
forces)..
A cell may in several respects be interpreted
as inversion of n atom (see further The
Cell).
Inner, underlying level unity gets also according to the
model "inverted" to outer potentials, expressed
as bonds, in lower d-degree (as "polarized" photons
in quantum mechanics?) It's like the more fundamental history
when fusion in the sun gets outsourced and "inverted"
to molecular constructions on the Earth. The big step from
the atomic level to a cell and outer atomic relations implies
an immense increase in degrees of freedom, even if already
a C-atom has several (cf. CO2 and the
steps between sp3- and sp2-hybridizations).
One aspect on the problematic demarcation
of cell units becomes the negative curvature inwards as a
reversal of the relations mass - space, between elementary
forces
FA - FG in macrocosm,
Mass built-in into Space, to Space into Mass in microcosms
of cells. Cf. in Embryology
the "blow up" of morula to a demarcating surface
as a step center to anticenter, followed by involutions.
About forces, protons and electrons, H+ and e-
that represent most of mass and most of space respectively
in the atom, become "carriers of forces", in the
same sense as bosons on the physical level (the assumed gravitons
and photons etc.) As responsible for elementary chemical processes
and bonds in cells they appear as poles 1a — 1b (+ /
- ½) in last step of the model, defining the
d-degree of motions
in the dimension chain. The "pole exchange" in d-degree
0/00 implies also a kind of inversion in fundamental
directions.
With increasing complexity molecules as
enzymes and coenzymes become forces in the same physical sense
on superposed levels, polarizing - binding ones, "carriers"
of the vital force.
Aggregations of micells as P-lipids during different degrees
of density has been studied in search for an answer on demarcation
of cells. Actually, inversions seem to characterize lipid
layers according to studies of lipids in later decades, different
structures with P-groups of the lipids inwards or outwards
(Wikipedia).
This ability for inverting the structure
seems connected with the P-group, phosphorus with valence
5. With a dimensional interpretation of valences the d-degree
5 is polarized in center and anticenter and directions outwards/inwards
of d-degree 4 in our model. On the deep, atomic level the
phosphorus atom P with valence 5 could represent the basic
integrating force.
Cf. the similarity between bilayers of P-lipids
and DNA-structure, see file The Cell.
9. Pure geometrical views on demarcation:
With the view that dimensions and geometries make up the
basis of Nature, the laws for quantification and demarcations
become endogenous. There is for instance such things as the
observed and unexplained polarizations in H2-clouds
in macrocosm between hotter and colder regions. In nuclei
of atoms it's said that the positive charge at fusion toward
heavier atoms is built as in layers from outside inwards.
It could be examples of the anticenter pole 00 and inward
direction (pole 4a), representing the polarizing and quantifying
force in the basic definitions of our dimension model,
a. In simple geometrical terms the step 3 →> 2 in
the model (2 as the d-degree of surfaces) implies a polarization
of 3-dimensional volumes to enclosed/excluded room.
With a "haploid" view on a dimension
chain as developed between poles 0 and 00, the anticenter
pole 00 of d-degree 4 may be regarded as debranched, (figure
a below) meeting "the other way around" from
the end of the chain in inward direction.
Postulated in the model is that pole 4a,
inward direction get "circular" structure when transformed
to d-degree 3.
Fig Li-5-1, Li-5-2, Li-3-6-1
b. The hypothesis that a dimension chain can correspond to
angle steps of halvings towards increasingly narrow angles
leads also to a nearly closed unit. Figure b.
Cf. directions of potential bonds as decreasing angles: C→>N
→> O →> (H). Such development of
the 0-pole outwards in angle steps may also illustrate life
as "½" of the whole and the living
unit's communication with the environment.
(One could also assume such a process as
endogenous within single atoms, involving processes and structural
changes at the molecular level. One example is the sp3
→ sp2-hybridization of carbon.)
c. A different aspect on the creation of a demarcating cell
membrane concerns general conditions for level developments:
It's suggested in files about physics to regard level development
occurring through the middle step 3-2 in the dimension chain
(see figure at end of this file). One hypothesis is that such
a development should demand counter-direction from another,
equivalent 5-dimensional center for saturation to a superposed,
more substantiated level (figure c). Without such counter-direction
the process 2 → 1 → 0/00 should only lead
to repetition or energy lost to the external world.
It would be an interpretation in agreement
with Haldane's hypothesis about the cell as a fusion of two
"half-organisms".
In a double cell-membrane the lipids
meet with directions outwards/inwards, that's of Direction,
d-degree 4. (Compare that orbitals of the same sign bind to
each other. Overlapping of inward directed magnetic circular
fields may eventually define a new center?)
10. Substantiation:
A gradual substantiation through increasing complexity is
of coarse a necessary complement to geometrical models. What's
only "field lines", potentials or motions as pathways
are to regard as stepwise substantiated to molecular chains,
to pipes, to organelles etc. Foldings of "linear"
proteins to globular, 3-dimensional ones can illustrate increasing
complexity. Saturation through incorporation from other units
is another factor that builds structures of high d-degrees
from lower ones (as 1 + 1 = 2, 2 +2 = 3!).
There is the similar processes on the
level of human society: That which begins as wanderer's pathway
through trackless terrain, becomes gradually a track, becomes
a carriageway with inns, becomes a highway through communities
with entrances and exits, etceteras.
The need to get from suburbs to inner city,
to and fro, becomes a drawing that gets materialized in a
subway.
One example could be the periodic, linear
arrangement of filaments in collagen. Exactly how this works,
in scientifically accepted terms, is another question.
How could enzymes emerge, the very long
protein chains that effectively reduces the energy needed
for a certain reaction? An analogy to the industrial revolution
of manual work as it seems. The energy needed for a certain
reaction without enzymes is often illustrated as a curve,
a hill. Rather than believe enzymes as preexisting, it's easier
to imagine them as substantiation of this very curve, taken
as a real mold, then inverted to a hole for the key and lock
relation to substrata. Enzymes are forces in the cell, As
substantiated to proteins they are a "matrix" to
substrata, in that sense complementary poles, the "antimatter"
on this level. (Something like magnetic fields in relation
to electric fields.)
To store such a protein chain in the long
term memory of DNA should of course need a backward process
from amino acids to codons. (Or already, in some potential
form, existed within DNA.
11. DNA coding amino acids:
Unique to life is DNA (or RNA) and the coding system DNA →>
proteins. See The
Genetic Code and The
protein synthesis and file The
Cell. Here only a couple of annotations.
As molecules amino acids represent a higher d-degree than
the bases: the tetrahedrons with a central C-atom may be regarded
as center-displaced (or "inverted") to the ring-bound
C- and N-atoms in the codon bases; a step from sp3-
to sp2-hybridization of the C-atom. It corresponds
to a step d-degree 3 → 2 (or 4 to 3) outwards, from
radial to circular structure. Conceptually codes are
also secondary in relation to what is coded, as the written
alphabet relative to spoken sounds.
With regard to the molecular structures, the relation could
perhaps be illustrated in a dimension chain as in the figure
below: bases as from intervals equivalent with debranched
degrees meeting in synthesizing direction the other way around

Fig Li-5-DNA
In valences, the phosphorus atom P represents d-degree 5
(or rather something like a step 5-4 with one double-bonded
oxygen).
N and O with valences 3 and 2 represent
opposite ends of backbone chains in amino acids (and opposite
polarity in charge*) - and bonds through H-bridges between
complementary bases in DNA (here also such N - N bonds, 3--3,
in our model outer poles in d-degree 2).
*(Cf. EM-force
supposed developed in step 3 - 2 in our model.
In directions there are proteins outwards in the cell, structure-building
and transporting, RNA-, DNA- nucleotides inwards the center,
towards less mobility. (Cf. principle of stepwise building-in
of anticenter, the 00-pole, and the similar building in of
the animal pole to a nervous system in embryological development.)
One of the subject classes can serve as reference to the
other because they originate from the same basic structure
(of the type our 5-dimensional model here).
The figure above could be compared with numbers in the "ES-chain"
(from file The genetic code")
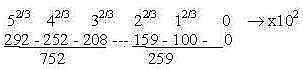 Fig Li-7
Fig Li-7
259 circa sum of 2 bound DNA-bases (G + C 262 - 2, A + T
261 - 2)
752 x 2 = sum of side-chains of amino acids for 20 + 4 codons.
2(5 + 4 + 3) = 24 amino acids.
We have also that 292 = P~P-ribose bound (2 x 98 + 150 -
3 x 18) and 252 + 208 = 2 x P~ ribose at which codon bases
get attached when constructed. Cf. a figure in S. Copley
et al* (2005) where such a pair of nucleotides are bound
to a P~P-ribose group. Their hypothesis is that amino acids
originally were constructed at the inner ribose which should
imply at the center of the chain in the figure above.)
*Copley S D, Smith E, Morowitz
H J: A mechanism for the association of amino acids with their
codons and the origin of the genetic code. Proc. Natl. Acad.
Sci. 2005, 102:4442-4447.
12. Additional remarks:
- The physical quantities (rather qualities) and their transformations
into one another as a dimension chain are naturally given
as aspects:
density - forces - mass/space
- charge - distance - time,
in accordance with definitions proposed in files on physics..
"Density" seen as the primary
quality in d-degree step 5 →4, polarized in mass/space
in step 4 →3. (Mass numbers become an underlying level
in relation to charge numbers for instance.)
- The underlying scheme and geometrical, mathematical rules
that is assumed with the model here, guiding the building
of molecules and organs on superposed levels could be imagined
as changing between d-degrees and levels in agreement with
these. (And the processes go further and further perhaps just
because relations and numbers don't become integers!)
Chemical processes could be apprehended as efforts of a fragmented
matter to solve the demand of the Whole, the "Entirety",
the ultimate binding force.
A level chain:

Fig Li-10-017
|
 Fig
Li-4-6-2
Fig
Li-4-6-2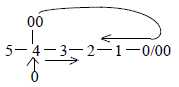


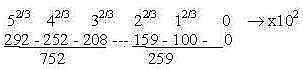 Fig Li-7
Fig Li-7